Appearance
Executive summary: In Belgium, a collaborative effort between regional and federal authorities has led to the creation of a unified service that aggregates all Belgian addresses into a comprehensive dataset. This dataset is called BeStAddress.
API Houte-Si-True

Houte Si True
API Development with FastAPI
The HouteSiTrue API was developed using FastAPI, a modern, fast web framework for building APIs with Python. The API serves as a bridge between our legacy GEOG system (or any other address system) and the BestAddress reference dataset, providing efficient address lookup and matching capabilities.
Core Components
- Router Structure The API is organized using FastAPI's router system, with the main address-related endpoints grouped under the
/addressesprefix:
python
router = APIRouter(prefix="/addresses", tags=["addresses"])- Key Endpoints
- Single Address Lookup: Retrieve address details by unique identifier
- Street Listings: Get streets by postcode or municipality
- Address Matching: Find the best match for given address components
- Batch Processing: Handle multiple address lookups in a single request
- Distance Calculations: Compute distances between geographical locations
- Similar Street Names: Find similar street names within a specified area
Address Matching Logic
The core functionality revolves around the address matching system, which uses both strict and fuzzy matching. The implementation combines FastAPI endpoints with sophisticated SQL queries for accurate address matching:
python
class AddressRequest(BaseModel):
postcode: str
streetname: str
house_number: str
box_number: str
@router.post("/bestmatch", operation_id="find_bestmatch_for_address")
async def find_bestmatch_for_address(body: AddressRequest, request: Request):
"""
Retrieve the best match for an address.
- postcode: strict matching
- street_name: fuzzy matching
- house_number: strict matching
- box_number: strict matching
"""
results = await find_address.bestmatch(body, request)
return resultsUnder the hood, the bestmatch function utilizes a SQL query that implements fuzzy matching using Levenshtein distance and Jaro similarity scores:
sql
SELECT
count(*) AS addresses_count
, street_id
, municipality_id
, lower(strip_accents(streetname_fr)) as streetname_fr_striped
, lower(strip_accents(streetname_nl)) as streetname_nl_striped
, lower(strip_accents(streetname_de)) as streetname_de_striped
, default_streetname
, greatest(
1 - (
levenshtein(streetname_fr_striped, '{street_name}') / greatest(length(streetname_fr_striped), length('{street_name}'))),
1 - (levenshtein(streetname_nl_striped, '{street_name}') / greatest(length(streetname_nl_striped), length('{street_name}'))),
1 - (levenshtein(streetname_de_striped, '{street_name}') / greatest(length(streetname_de_striped), length('{street_name}')))
) AS best_levenshtein_score
, greatest(
jaro_similarity(streetname_fr_striped, '{street_name}'),
jaro_similarity(streetname_nl_striped, '{street_name}'),
jaro_similarity(streetname_de_striped, '{street_name}')
) AS best_jaro_score
FROM bestAddress
WHERE 1=1
AND postcode = '{postcode}'
AND best_jaro_score > 0.6
GROUP BY ALL
ORDER BY best_levenshtein_score DESC
LIMIT 3;python
return {
"is_perfect_match": is_perfect_match,
'is_partial_match': is_partial_match,
"street_id": addresses[0]["street_id"],
"municipality_id": addresses[0]["municipality_id"],
"address_id": addresses[0]['address_id'],
"levenshtein_score": results[0]["best_levenshtein_score"],
"matches": addresses
}This query performs several key operations:
- Strips accents and normalizes street names in all three national languages (French, Dutch, and German)
- Calculates Levenshtein distance scores for each language version
- Computes Jaro similarity scores as a secondary matching metric
- Filters results based on a minimum similarity threshold
- The SQL returns the top 3 matches ordered by Levenshtein score
- The Python code returns the best match and the matches found by the SQL query
Application Configuration
The API is built with scalability and maintainability in mind:
python
def get_application() -> FastAPI:
application = FastAPI(
title=metadata.app_name,
description=metadata.base_description,
version=os.getenv("CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA", "N/A"),
openapi_tags=metadata.tags_metadata,
contact=metadata.contact,
deployement=metadata.deployement,
)Model-Context-Protocol (MCP)
We implemented a Model-Context-Protocol (MCP) pattern using FastApiMCP, to be able to call the API from LLM with tools capabilities.
python
mcp = FastApiMCP(app)Performance Considerations
The API includes performance monitoring features:
- Execution time tracking for each request
- Batch processing capabilities (up to 25 addresses per request)
- Efficient distance calculations using the
geopylibrary (spatial extension from DuckDB could also be used)
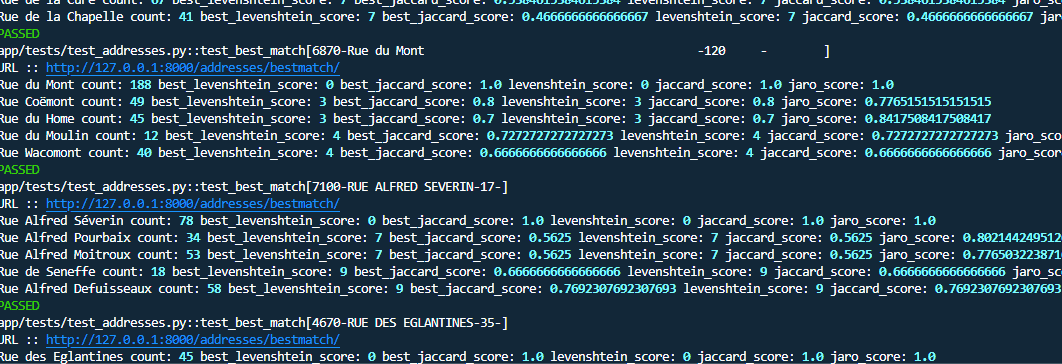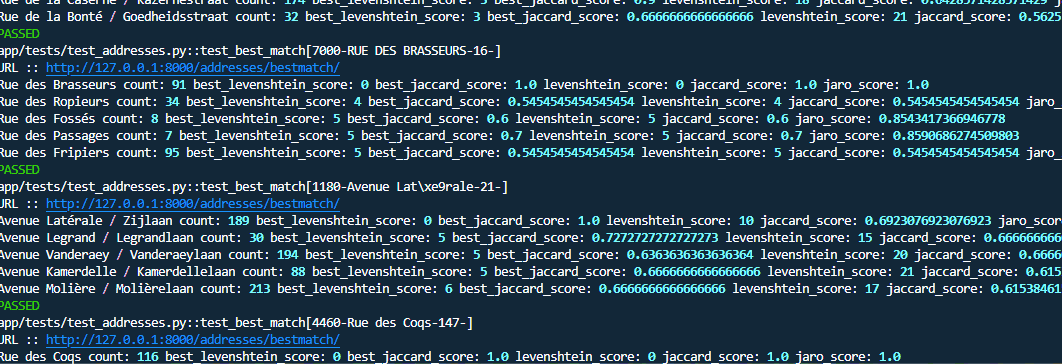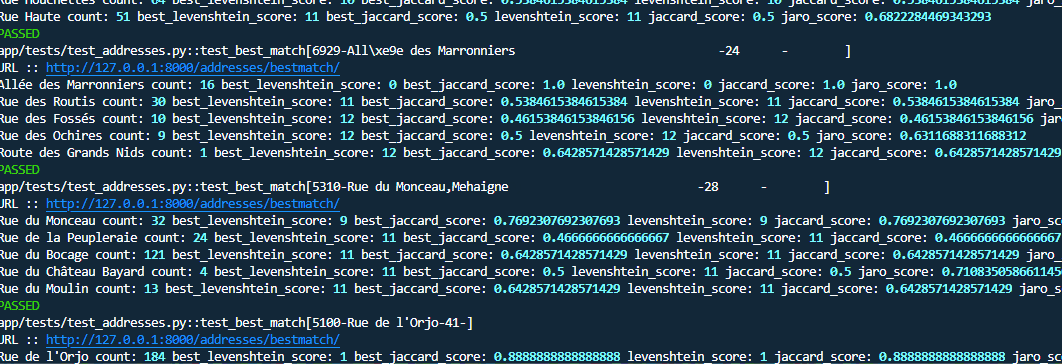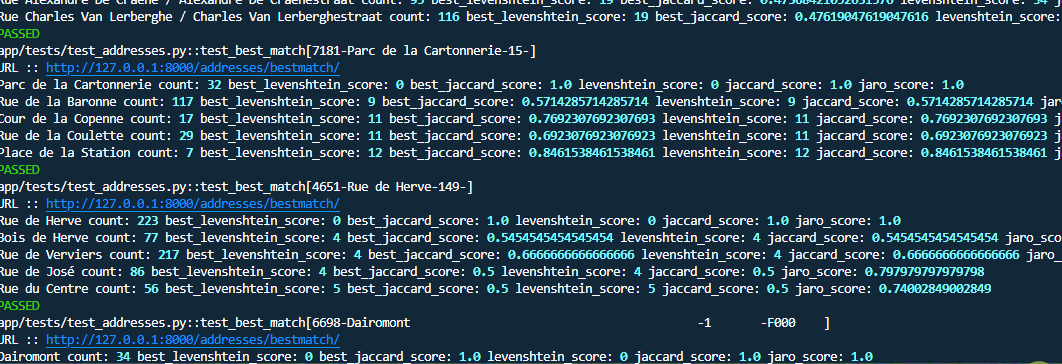
Performance checks
Error Handling and Validation
The API implements robust error handling and input validation:
- Input validation through Pydantic models
- Batch size limitations
- Proper error responses for invalid requests
Conclusion
The HouteSiTrue API provides a robust and efficient solution for address matching and validation in Belgium. By combining strict and fuzzy matching techniques with a well-structured API design, we've created a reliable service that bridges the gap between legacy systems and modern address data requirements.
If anyone from public administration is interested in using this API, please reach out to us. We are happy to share the code and help you set it up.
This API was used to match addresses from our legacy GEOG system with the BestAddress reference dataset. For that we used the bestmatch endpoint in combination with an orchestrator.
Dagster bestmatch